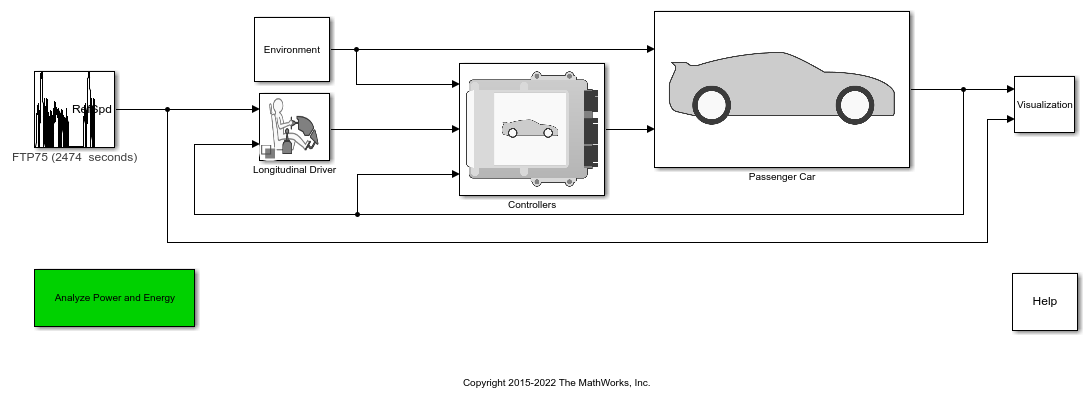
Transmission and Drivetrain
Transmissions, torque converters, differentials, and controllers
In powertrains, the transmission and drivetrain comprise the driveline. Transmissions convert engine torque to drive shaft torque. Drivetrains convert the drive shaft torque to axle torque. Use the transmission and drivetrain blocks to assemble drivelines for torque capacity sizing and gear ratio impact on performance.