grabcut
Segment image into foreground and background using iterative graph-based segmentation
Syntax
Description
BW= grabcut(___,Name,Value)
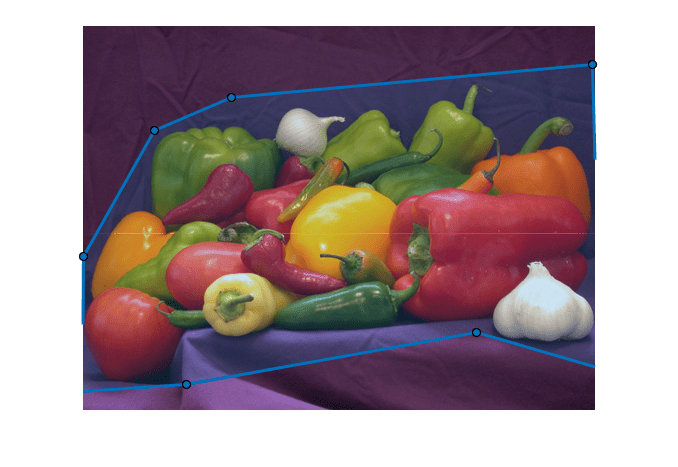
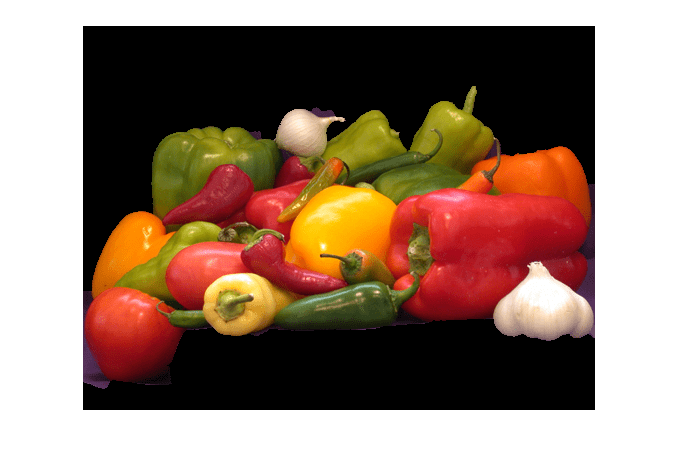
Examples
输入参数
Output Arguments
Tips
For
doubleandsingleimages,grabcutassumes the range of the image to be[0 1]. Foruint16,int16, anduint8images,grabcutassumes the range to be the full range for the given data type.For grayscale images, the size of
L,foremask, andbackmaskmust match the size of the imageA. For color and multi-channel images,L,foremask, andbackmaskmust be 2-D arrays with the first two dimensions identical to the first two dimensions of the imageA.
Algorithms
The algorithm treats all subregions fully or spatially outside the ROI mask as belonging to the background. To get an optimal segmentation, make sure the object to be segmented is fully contained within the ROI, surrounded by a small number of background pixels.
Do not mark a subregion of the label matrix as belonging to both the foreground mask and the background mask. If a region of the label matrix contains pixels belonging to both the foreground mask and background mask, the algorithm treats the region as unmarked.
该算法假设r之外的所有条件egion of interest belong to the background. Marking one of these subregions as belonging to foreground or background mask has no effect on the resulting segmentation.
References
[1] Rother, C., V. Kolmogorov, and A. Blake. "GrabCut - Interactive Foreground Extraction using Iterated Graph Cuts".ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH). Vol. 23, Number 3, 2004, pp. 309–314.